algorithm - STL C++
is_sorted_until()
Declaration
template <class FwdIterator> FwdIterator is_sorted_until( FwdIterator xFirst, FwdIterator xLast );
Description
This function determines the range of entries starting at "xFirst" up to the one before "xLast" that are sorted and returns an iterator that points to the last entry in the sorted range. In the overloaded version, the function "xComp" is used as the ordering function.Header Include
#include <algorithm>
Overloads
template <class FwdIterator, class BinaryPredicate> FwdIterator is_sorted_until( FwdIterator xFirst, FwdIterator xLast, BinaryPredicate xComp );
Example
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
// Create a vector instance
vector<char> qV;
qV.push_back('X');
qV.push_back('o');
qV.push_back('a');
qV.push_back('X');
qV.push_back('.');
qV.push_back('n');
qV.push_back('e');
qV.push_back('t');
vector<char>::iterator qEndOfSort;
vector<char>::iterator qIter;
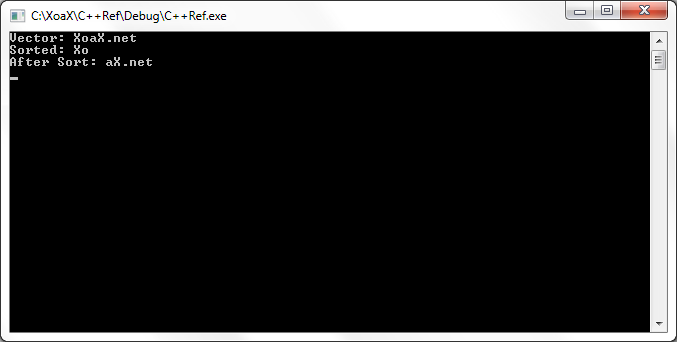
cout << "Vector: ";
for (qIter = qV.begin(); qIter != qV.end(); ++qIter) {
cout << *qIter;
}
cout << endl;
// Find the end of the sorted items
qEndOfSort = is_sorted_until(qV.begin(), qV.end());
++qEndOfSort;
cout << "Sorted: ";
for (qIter = qV.begin(); qIter != qEndOfSort; ++qIter) {
cout << *qIter;
}
cout << endl << "After Sort: ";
for (qIter = qEndOfSort; qIter != qV.end(); ++qIter) {
cout << *qIter;
}
cout << endl;
// Keep the window open
cin.get();
return 0;
}Output
© 2007–2024 XoaX.net LLC. All rights reserved.
