Image Processing Computer Science
Convert Grayscale Image via Otsu Threshold
This Image Processing Reference section displays the code for an example program that demonstrates how to convert a grayscale image that is ideally bimodal to a black and white image via the Otsu threshold calculation.
The Otsu algorithm is best suited to images with a bimodal distribution of pixel values: values that fall into to normal curves. Recall that the mean of a Gaussian distribution is calculated by summing the values and dividing by the number of values in the distribution. Here, we collect the pixel values into groups and multiply by the count within each group. That is, we sum the pixel values times the number of that pixel value in the image divided by the number of pixels in the image.
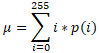
where
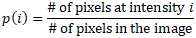
Using this formula for the probability of an intensity, we can calculate the variance, or the overall spread, of the intensities of the entire image as
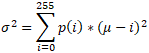
What we would like to do is minimize the spread of the variance for each of the two classes in the image. This value is calculated as the weighted sum of the variance of each class:
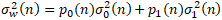
Class 0 contains the dark pixels of the image and its variance is given as
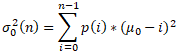
where its mean is calculated as
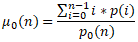
and its associated probability is
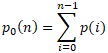
Similarly, for the class of light pixels, we have
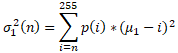
where its mean is calculated as
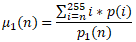
and its associated probability is
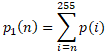
Minimizing the within class variance is the same as maximizing the between class variance:
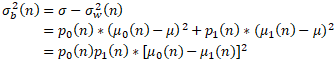
To make the updates easier, we note that the following relationship for the sum of the classs probabilities:
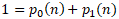
Also, we have this relationship that for the sum of the means that makes use of the overall mean:
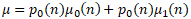
The values for class zero can be updated quickly, using these formulas for the probability of class 0
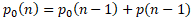
and the mean of class 0
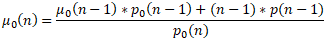
Using the sum formulas and the probability and mean of class 00, we can update the probability of class 1
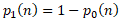
and the mean of class 1
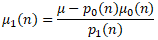
OtsuThreshold.php
<?php
function CreateOtsuThreshImage($qGrayScaleImage) {
$iW = ImageSX($qGrayScaleImage);
$iH = ImageSY($qGrayScaleImage);
$qBlackWhiteImage = ImageCreate($iW, $iH);
// Allocate the black and white colors
$iBlack = ImageColorAllocate($qBlackWhiteImage, 0, 0, 0);
$iWhite = ImageColorAllocate($qBlackWhiteImage, 255, 255, 255);
// Create a histogram of colors from the image
$iaHistogram = Array();
// Initialize the histogram to all zeros
for ($iGray = 0; $iGray < 256; ++$iGray) {
$iaHistogram[$iGray] = 0;
}
// Increment the correct histogram bin for each pixel
for ($j = 0; $j < $iH; ++$j) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $iW; ++$i) {
$iColor = ImageColorAt($qGrayScaleImage, $i, $j);
// Since the color is gray, we can just take the blue channel
$iColor &= 0xFF;
// Increment the color
$iaHistogram[$iColor] += 1;
}
}
$iPixelCount = $iW*$iH;
$dPixelCount = DoubleVal($iPixelCount);
$iFirstNonZero = -1;
$iLastNonZero = 0;
$daProbabilities = Array();
$dMean = 0.0;
// Find the first and last histogram colors that are nonzero.
for ($iGray = 0; $iGray < 256; ++$iGray) {
// The probability for each gray value. Division is floating-point.
$daProbabilities[$iGray] = $iaHistogram[$iGray]/$dPixelCount;
$dMean += $daProbabilities[$iGray]*$iGray;
if ($iaHistogram[$iGray] > 0) {
if ($iFirstNonZero == -1) {
$iFirstNonZero = $iGray;
}
$iLastNonZero = $iGray;
}
}
// The threshold is the lowest value of the higher class
// Run over all possible values
// To minimize within class variance, maximize between class variance
// Winthin class variance Vw = P0*V0 + P1*V1
// Between class variance
// Vb = V - Vw
// = P0*(M0 - M)^2 + P1*(M1 - M)^2
// = P0*P1*(M0 - M1)^2, since M = P0*M0 + P1*M1 and P0 + P1 = 1
// The probability of each class is the sum of its probabilities
$dP0 = 0.0;
$dP1 = 1.0;
$dMean0 = 0.0;
$dMean1 = 0.0;
$iThreshold = 0;
// $iT is the last value of the lower class. The threshold is one more than it.
$iT = $iFirstNonZero;
$iVarB = 0.0;
$dMaxVarB = 0.0;
do {
$dOldP0 = $dP0;
// Note that the sum of the probabilities is always one: P0 + P1 = 1
$dP0 += $daProbabilities[$iT];
$dP1 = 1.0 - $dP0;
// Adjust the mean of the first class
$dMean0 *= $dOldP0;
$dMean0 += ($daProbabilities[$iT]*$iT);
$dMean0 /= $dP0;
// Also, for the overall mean: M = P0*M0 + P1*M1
// So, M1 = (M - P0*M0)/P1
$dMean1 = ($dMean -($dP0*$dMean0))/$dP1;
// Vb = P0*P1*(M0 - M1)^2
$dMeanDiff = ($dMean0 - $dMean1);
$dVarB = $dP0*$dP1*$dMeanDiff*$dMeanDiff;
if ($dMaxVarB < $dVarB) {
$dMaxVarB = $dVarB;
$iThreshold = ($iT + 1);
}
++$iT;
} while($iT < $iLastNonZero);
// Use the threshold to set the values for the black and white image
for ($j = 0; $j < $iH; ++$j) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $iW; ++$i) {
$iGrayPixel = ImageColorAt($qGrayScaleImage, $i, $j);
$iGrayPixel &= 0xFF;
if ($iGrayPixel < $iThreshold) {
ImageSetPixel($qBlackWhiteImage, $i, $j, $iBlack);
} else {
ImageSetPixel($qBlackWhiteImage, $i, $j, $iWhite);
}
}
}
return $qBlackWhiteImage;
}
$qOriginalImage = ImageCreateFromPng("FirstMourning_Bourguereau.png");
$qOtsuImage = CreateOtsuThreshImage($qOriginalImage);
$iW = ImageSX($qOriginalImage);
$iH = ImageSY($qOriginalImage);
$qCompareImage = ImageCreateTrueColor($iW, 2*$iH);
// Copy the original image and the gray scale image
ImageCopyMerge($qCompareImage, $qOriginalImage, 0, 0, 0, 0, $iW, $iH, 100);
ImageCopyMerge($qCompareImage, $qOtsuImage, 0, $iH, 0, 0, $iW, $iH, 100);
Header('Content-type: image/png');
ImagePng($qCompareImage);
ImageDestroy($qCompareImage);
ImageDestroy($qOriginalImage);
ImageDestroy($qOtsuImage);
?>
Output
© 2007–2024 XoaX.net LLC. All rights reserved.
